Stay up to date with the latest news, announcements, and articles.
Creating a Bitcoin wallet address involves generating a public-private key pair, where the public key forms the address and the private key controls access to the funds. Security is paramount: if the private key is lost or compromised, the associated funds may be irretrievable. This article provides a scientific and research-focused overview of Bitcoin wallet addresses, including their types, creation processes, and best practices for safeguarding digital assets.
What is a Bitcoin Wallet Address?
A Bitcoin wallet address is an alphanumeric string derived from a user’s public key that enables the sending and receiving of Bitcoin. It does not reveal the private key, ensuring that the owner’s funds remain secure. For example:
- A wallet address is similar to an account number in traditional finance.
- It serves as a destination for transactions.
- The bitcoin address length typically ranges from 26 to 35 characters.
A common question among new users is what is BTC wallet address, which refers to the unique identifier used to send and receive Bitcoin. People also often ask what is a BTC wallet address, seeking to understand how it links their transactions on the blockchain. In casual conversations, many phrase it as what’s a Bitcoin wallet address, all pointing to the same essential component of cryptocurrency management.

Types of Bitcoin Wallet Addresses
Bitcoin addresses have evolved alongside protocol upgrades. The most common types are:
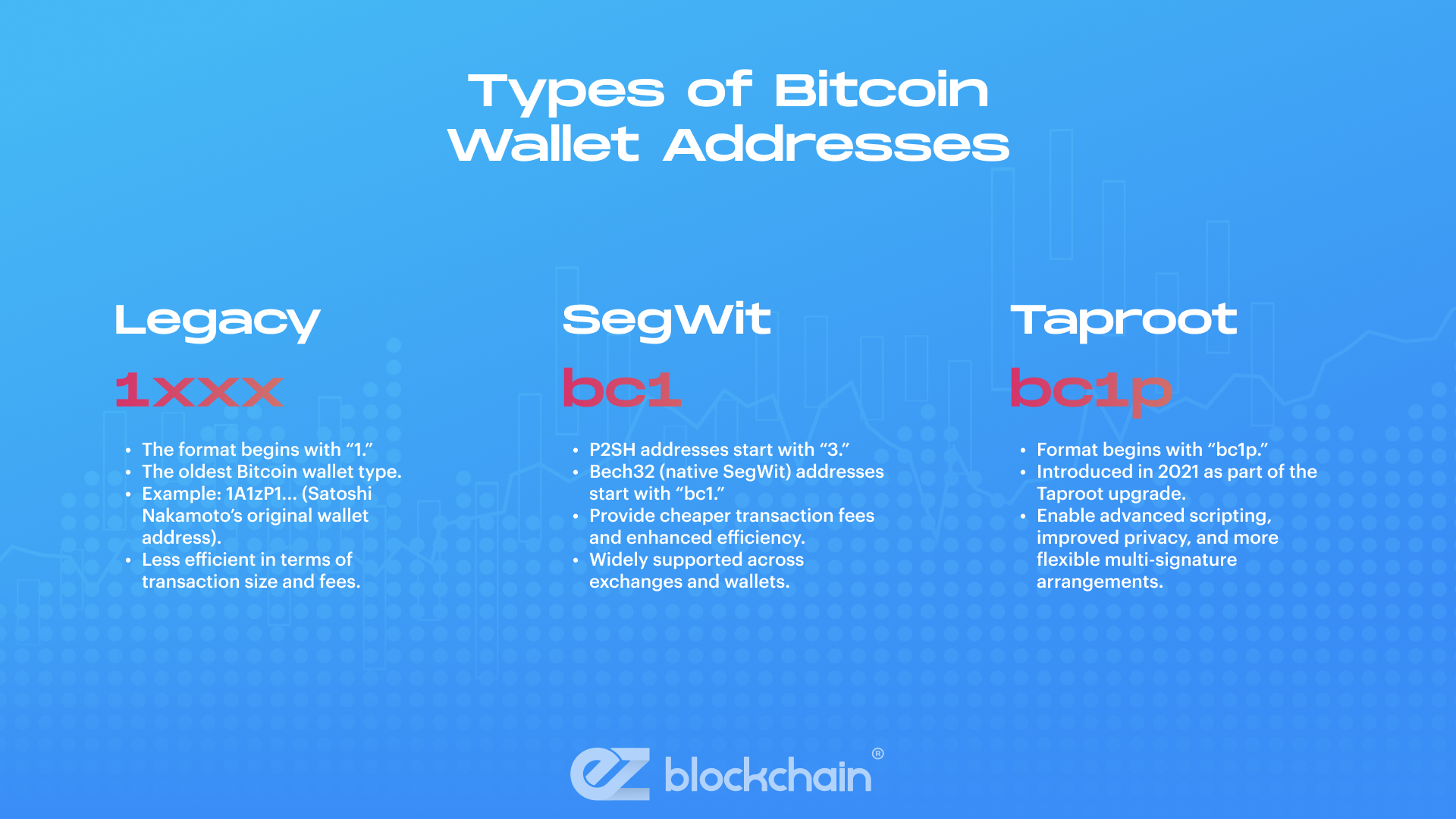
Legacy (P2PKH) Addresses
- The format begins with “1.”
- The oldest Bitcoin wallet type.
- Example: 1A1zP1… (Satoshi Nakamoto’s original wallet address).
- Less efficient in terms of transaction size and fees.
SegWit (P2SH and Bech32) Addresses
- P2SH addresses start with “3.”
- Bech32 (native SegWit) addresses start with “bc1.”
- Provide cheaper transaction fees and enhanced efficiency.
- Widely supported across exchanges and wallets.
Taproot (P2TR) Addresses
- Format begins with “bc1p.”
- Introduced in 2021 as part of the Taproot upgrade.
- Enable advanced scripting, improved privacy, and more flexible multi-signature arrangements.
“Taproot addresses improve scalability and security by merging multiple scripts into a
single public key, significantly reducing transaction data size [2].”
What is the btc wallet address with Taproot? The implementation of Taproot in Bitcoin introduced significant enhancements in scalability and security by consolidating multiple scripts into a single public key. This advancement allows for more complex transactions, such as multi-signature arrangements and smart contracts, to appear as standard single-signature transactions on the blockchain.
As a result, the underlying complexity of these transactions is obscured, improving privacy and reducing the data footprint on the blockchain. This approach not only optimizes block space but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the Bitcoin network. By streamlining transaction processing and enhancing privacy, Taproot facilitates a more scalable and secure environment for Bitcoin transactions.
Taproot’s integration of Schnorr signatures enables signature aggregation, allowing multiple signatures to be combined into a single signature. This aggregation reduces the amount of data required for transaction validation, leading to lower transaction fees and increased throughput. The combination of these features underscores Taproot’s role in improving the scalability and security of the Bitcoin network, making it more efficient and user-friendly.
How to Create a Bitcoin Wallet Address
Creating a wallet address involves selecting a wallet solution, generating keys, and ensuring security. The process can be divided into:
Choosing a Wallet
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices offering maximum security (e.g., Ledger, Trezor).
- Software Wallets: Mobile or desktop apps suitable for everyday use.
- Exchange Wallets: Provided by cryptocurrency exchanges, though less secure due to centralized risks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Wallet Address
- Select a Wallet Provider – Decide between hardware, software, or exchange.
- Install/Initialize the Wallet – Download the software or set up the hardware.
- Generate Seed Phrase – A private backup phrase crucial for recovery.
- Create a Public Address – The wallet generates a unique Bitcoin address.
- Backup and Secure – Store seed phrases securely offline.
This sequence ensures that users understand what is wallet address for Bitcoin and how to safely create one.

Understanding Wallet Address Formats
Different address formats exist due to Bitcoin’s upgrades. Key aspects include:
- Legacy (P2PKH): Long-standing, but higher fees.
- SegWit (P2SH, Bech32): Lower transaction costs, higher efficiency.
- Taproot (P2TR): Advanced privacy and flexibility.
The choice depends on wallet compatibility, transaction needs, and security preferences. Users often ask what’s wallet address or what’s btc wallet address, and the answer depends on which format they are using.
“Wallet addresses are not static; multiple addresses can be generated from a single
seed to enhance privacy and security [3].”
Furthermore, the BIP44 standard builds upon BIP32 by introducing a structured path for key derivation, facilitating the management of multiple cryptocurrencies and accounts within a single wallet. This hierarchical structure not only simplifies backup procedures but also enhances privacy and security by organizing keys in a tree-like structure, making it easier to manage and recover digital assets.
In summary, the ability to generate multiple addresses from a single seed phrase, as enabled by HD wallets and standards like BIP32 and BIP44, significantly contributes to the privacy, security, and manageability of cryptocurrency holdings.
Security Tips for Managing Bitcoin Wallet Addresses
Proper security practices are critical when managing wallet addresses. Here are essential strategies:
- Backup Seed Phrase – Store in multiple offline locations.
- Enable Encryption – Use strong encryption for wallet software.
- Use Hardware Wallets – Reduce exposure to malware.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi – Prevent interception of sensitive data.
- Rotate Addresses – Generate new addresses for transactions to preserve privacy.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) – Particularly on exchange wallets.
While Bitcoin addresses are public, private keys must remain confidential to maintain full control over cryptocurrency.
Monitoring Wallet Performance with the EZ Blockchain Dashboard
Managing multiple addresses and monitoring transactions can be complex. The EZ Blockchain Dashboard allows users to:
- Track all wallet balances in real time.
- Monitor incoming and outgoing transactions.
- Integrate multiple wallet types (hardware, software, and exchange).
- Strengthen oversight with built-in security alerts.
- Simplify the process of identifying address activity.
By consolidating wallet monitoring into one platform, users improve both convenience and security.
| Address Type | Format | Transaction Fees | Compatibility | Security Features |
| Legacy (P2PKH) | Starts with “1” | Higher fees | Universally supported | Basic security |
| SegWit (P2SH) | Starts with “3” | Lower fees | Broadly supported | Better efficiency |
| SegWit (Bech32) | Starts with “bc1” | Lowest fees | Increasing support | Enhanced security |
| Taproot (P2TR) | Starts with “bc1p” | Lowest fees + advanced features | Limited but growing support | Advanced privacy & scripting |
In conclusion, the EZ Blockchain Dashboard offers a streamlined solution for managing the complexity of multiple Bitcoin addresses and transactions. By providing real-time balance tracking, transaction monitoring, and integration across wallet types, the platform enhances both convenience and security for users. When combined with an understanding of the different address types—from Legacy bitcoin address and SegWit to Taproot—users can optimize transaction fees, improve privacy, and take full advantage of advanced blockchain features, making efficient wallet management both practical and secure.
Conclusion
Expanding on this, the dynamic nature of Bitcoin wallet addresses—where multiple addresses can be generated from a single seed—further enhances user privacy and mitigates the risks of address reuse. Advanced formats such as SegWit and Taproot not only reduce transaction fees and improve scalability but also enable complex scripting capabilities that can support multi-signature wallets and smart contracts, adding layers of security and functionality.
Moreover, tools like the EZ Blockchain Dashboard empower users to manage and monitor multiple addresses efficiently, providing real-time insights, alerts for unusual activity, and compatibility across hardware, software, and exchange wallets. By combining careful wallet selection, adherence to security best practices, and effective monitoring, users can confidently engage in cryptocurrency transactions while minimizing risk, ultimately strengthening their participation in the decentralized financial ecosystem.
Fill out a form and our bitcoin mining expert will contact you.
FREE CONSULTATIONchoose
a miner
profit and
understand data?
business remotely
with EZ Blockchain?
Fill out a form and our bitcoin mining expert will contact you.









