Stay up to date with the latest news, announcements, and articles.
See, these questions don’t really have straightforward answers — the Bitcoin stock depends on several variables. These include your own Bitcoin mining output, the fixed 21 million Bitcoin supply, regularly changing mining difficulty, and different mining approaches.
Let’s explore each, finding out how all of these essential aspects influence your mining profitability along the way.
Key Factors That Determine How Many Bitcoins You Can Mine
Bitcoin’s coin generation cap is a very flexible, liquid thing that can bring different fruits for differently-equipped miners. There are a couple of baseline factors that set the cap on how many bitcoins you can mine per day.
Mining hardware
Hardware is one of the most critical components in Bitcoin mining. In the early days, miners could use personal computers or GPUs, but modern mining demands specialized equipment.
- ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) are the current standard for Bitcoin mining. Designed specifically for mining, ASICs outperform general-purpose hardware in terms of efficiency.
- Higher-performance hardware means a higher hash rate (computing power), which increases the likelihood of mining Bitcoin successfully.

Hash rate and performance
The hash rate is the reading that indicates how much computational power your mining machine dedicates to solving Bitcoin’s cryptographic puzzles (i.e., how fast and efficiently it mines in general).
- Higher hash rates allow miners to solve blocks faster, boosting their chances of earning Bitcoin rewards.
- Mining hardware’s hash rate sets the number of calculations per second performed by a machine.
Energy consumption and efficiency
Another pillar of mining operations is energy and the way one’s mining rig consumes it. Energy costs can significantly impact profits, as high-performance ASICs consume large amounts of power.
- Mining efficiency is often measured as joules per terahash (J/TH) — the energy consumed per unit of computational power. Lower J/TH values indicate better efficiency.
- As energy prices vary by region, miners in low-cost energy areas have an advantage in profitability.
The 21 Million Bitcoin Cap
To keep things ultimately specific, yes, is there a bitcoin limit? There absolutely is.
To keep things ultimately specific, yes, there is a fixed cap for Bitcoin’s overall supply. Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million, which serves as more than a plain indication number — this is a unique characteristic of the coin that highlights exactly how valuable and scarce Bitcoin is.
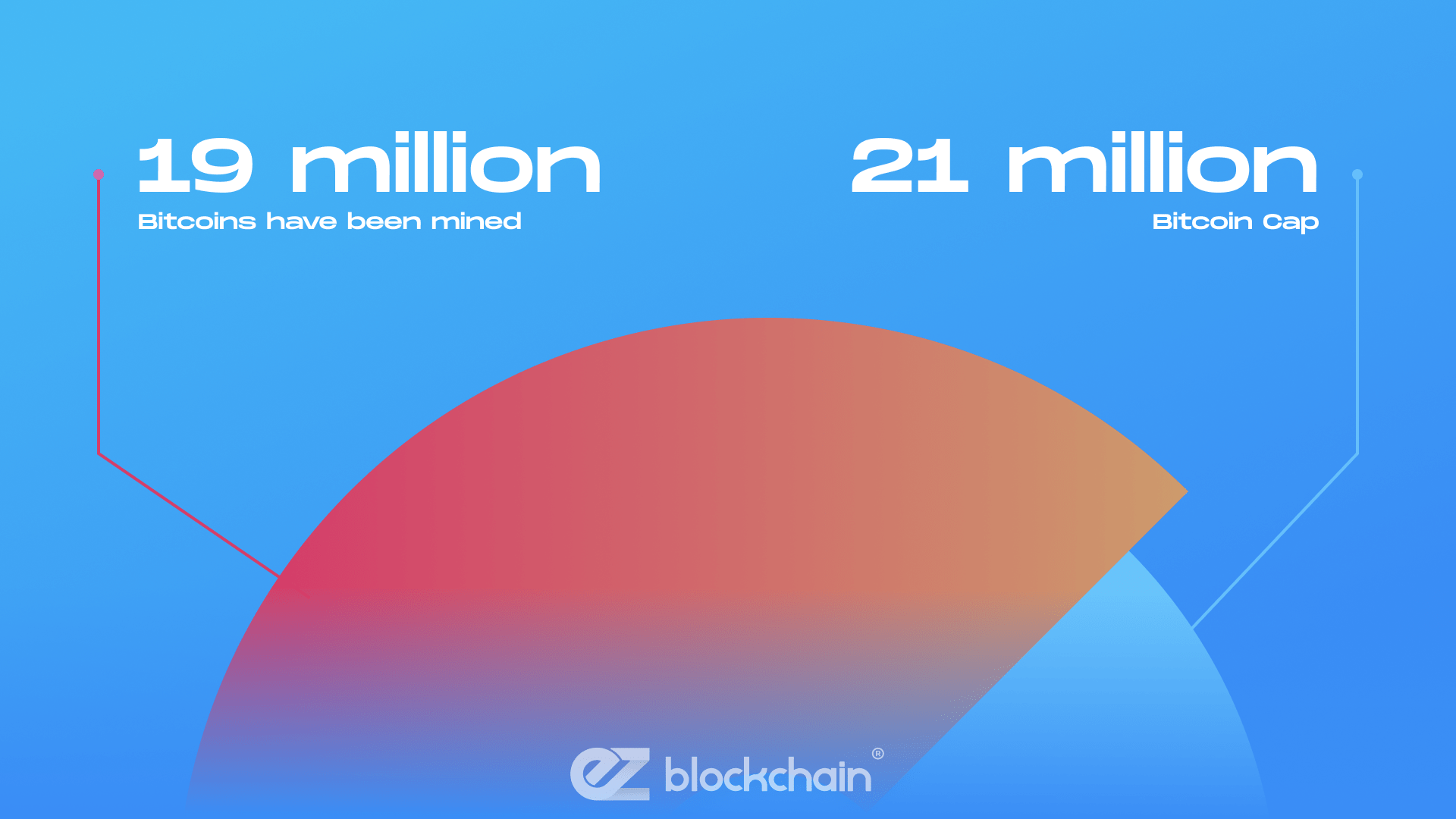
This cap limits the number of Bitcoins that can ever exist. But up to date, around 19 million Bitcoins have been mined, which leaves us about 2 million available to be mined over the coming decades. The cap also helps create and manage a deflationary system, where mining is made progressively more challenging as fewer Bitcoins remain to be mined. How much bitcoin can I mine, and at which point could they deplete?
Mining Difficulty and Its Impact
Mining difficulty is the essential mechanism that helps the Bitcoin network regulate how much bitcoin can you mine, and at what rate of success. To balance out the possible speed of mining (at the highest available hash rate), the mining difficulty must be regularly re-adjusted. Based on the network’s overall activity and rates of mining success, the difficulty is tweaked and slightly increased approximately every two weeks.
The difficulty grows as more miners join the network, grabbing more chunks of Bitcoin at faster rates. A lot also depends on how often a block is mined. The difficulty increase helps slow down the coin’s production rate in order to maintain a balanced block mining rate — one block mined every 10 minutes on average.
The mining difficulty has been growing through the years, making it harder for miners to earn Bitcoins as competition grows. However, with good, regularly upgraded hardware, insightful energy maintenance, and crypto mining hosting services, miners can take on these adjustments and actually turn them profitable in the long run.
Pool Mining Vs. Solo Mining: Which Yields Better?
On top of strictly technical specifics and limitations, the exact approach one adopts — solo or collaborative mining — also defines how many Bitcoin blocks are mined per day by one’s machine.
Bitcoin miners can operate individually, setting off for solo mining with their own rig, relying on their own powers and ambitions only. Or they can join pre-structured mining pools where miners gather and combine computational resources to mine blocks collaboratively. Each approach has its advantages and trade-offs:
- Solo mining:
- You get full rewards for block discovery;
- There is higher variability in earnings due to competition with large mining operations;
- There are also higher risks, as individual miners compete against large-scale operations.
- Pool mining:
- You get smaller yet consistent earnings, with rewards being shared among all pool members;
- Overall risks are lower, as the combined hash rate serves to boost the chances of mining blocks;
- A popular headstart choice with individual miners who are limited in their hash rate powers.
Takeaway: For most miners today, pool mining provides more predictable earnings, as the individual hash rate of solo miners typically cannot compete with large mining farms. So picking a good pool is always a good headstart, while solo mining should only be leveraged when you have the budget and tech capacity.
Estimating Your Bitcoin Mining Earnings
In order to calculate mining profits, we need to evaluate hardware costs, hash rate, energy expenses, and mining difficulty.
- BTC price: A fluctuating Bitcoin price directly affects mining returns.
- Electricity rates: Lower consumption rates improve profit margins.
- Mining pool fees: Many pools charge a small percentage for participation, which affects net earnings.
- Hardware depreciation: Over time, hardware becomes less efficient as newer technology enters the market.
You can use a specialized online calculator to estimate potential earnings by inputting these variables and getting a clearer picture of your potential returns.
Energy Costs vs. Mining Earnings: A Historical Analysis
Average rates of energy consumption have been affecting and shaping mining costs historically. With mining hardware consuming felt power, miners must weigh energy costs against Bitcoin earnings. Some concrete takeaways we can give here are these:
- During Bitcoin’s bull markets, higher prices can offset electricity costs.
- Conversely, during price drops, miners with high energy expenses may find it unprofitable to continue, which provokes some to temporarily halt all operations.
How Long Does it Take to Mine One Bitcoin?
The stretch of time required for mining one Bitcoin depends on the miner’s hash rate, the network’s mining difficulty, and other factors. On average:
- In a mining pool: Miners receive fractions of a Bitcoin regularly as the pool mines blocks, allowing individual miners to earn consistently based on their contributed hash rate.
- Solo mining: With average hardware, mining one Bitcoin individually could take years due to the high competition and difficulty.
In general, rather than taking “one Bitcoin” as a baseline for calculations, miners calculate their expected BTC earnings based on how many Bitcoins in a block there are, the block rewards, and the pool’s performance.
Conclusion: Mining Bitcoin Competitively
Mining Bitcoin has become a competitive process influenced by a bunch of variables. Here’s a quick recap:
- Hardware, hash rate, and energy efficiency are foundational to mining success.
- Mining pools offer smaller, consistent earnings, while solo mining provides higher rewards but with more risk.
- The bitcoin limits and rising difficulty call for miners to be prepared for upgrades and optimizations.

For new miners, assessing energy costs and hardware efficiency is key. Mining Bitcoin can be profitable under the right circumstances, but as competition and difficulty increase, profitability requires strategic decisions on hardware, energy management, and mining approach. We can help you with all of that, saving time and hidden costs.
Fill out a form and our bitcoin mining expert will contact you.
FREE CONSULTATIONchoose
a miner
profit and
understand data?
business remotely
with EZ Blockchain?
Fill out a form and our bitcoin mining expert will contact you.









