Stay up to date with the latest news, announcements, and articles.
Initially, Bitcoin looked attractive in almost every aspect. Think about the unprecedented technology blockchain with unmatched security, privacy, and transparency and its ability to complete financial transactions without a centralized body or intermediaries. Both the private and public sectors quickly warmed up to the idea of cryptocurrency and integrated it into their financial dealings.

However, fast forward to 2022, and the future doesn’t seem so bright. The cryptocurrency space seems to be tumbling quicker than it emerged. We are in the middle of one of the greatest crypto sell-offs, with the industry losing more than half its value in less than six months. Bitcoin is also down more than 80% from its all-time high as crypto companies report record losses. Some are closing operations completely, while others like Binance and Coinbase resort to disabling Bitcoin withdrawals and laying off workers to survive the crisis.
For now, it’s hard to view Bitcoin and cryptocurrency as the future of finance. This article reflects on Bitcoin and explains what happened to the ‘21st-century gold.’
What Happened to Bitcoin?
According to a survey conducted on 2000 American adults, more than half of the US population believed that cryptocurrencies and digital assets are the future of finance. 68% of the respondents aged between 25 and 34 agreed that cryptocurrencies would be an integral part of their financial future. 61% of those aged between 35 and 44 also shared the same view.
Indeed, the trillion-dollar industry was hard to ignore for individuals, businesses, and institutional investors. First, Bitcoin appeared to have the potential to become the 21st century gold from its deflationary properties. Earlier reports claimed that Bitcoin delivered a 99.9% deflation, labeling it a potential hedge against inflation.
Second, Bitcoin is popularized as a decentralized digital currency that is not subject to any government or institutional interference. There is no central authority, which eliminates entry barriers like in the traditional financial system. As such, it would be a perfect solution for banking the unbanked, given that over 1.7 billion people remain unbanked.
Third, there has been a growing need for an accessible, secure, and transparent financial system over the past few years. People were losing confidence in fiat currencies and the traditional financial systems due to their inability to provide financial freedom and credibility. The rise of Bitcoin birthed the decentralized finance (DeFi) world that could offer more transparency, faster and cheaper transactions, and transactional security. DeFi quickly gained traction and became a whole industry with all financial services, including lending, borrowing, investing, and trading.
Finally, cryptocurrency proved to be an unprecedented store of value. The total supply of most cryptocurrencies is limited, with Bitcoin’s capped at 21 million coins. With its supply fixed, it means the scarcity will influence its value. Furthermore, Bitcoin proved to be a worthwhile investment after the news of overnight crypto millionaires broke.
The Dawning of Bitcoin’s Reality
Bitcoin has many attractions, the chief being allowing users to complete financial transactions using just their digital identities. They would not need fiat currency or trusted third parties like credit card companies or financial institutions. It relies purely on the innovative blockchain technology, in which all transactional information and user account balances are maintained on a public ledger.
The ledgers are maintained on multiple computers known as nodes, rendering them almost tamper-proof. They are also available to anyone with an internet connection, which creates a remarkable level of transparency. However, despite Bitcoin’s potential and innovative distributed ledger technology, it is faced with fundamental weaknesses that are getting in its way of becoming an acceptable medium of exchange and the future of finance.
Volatility
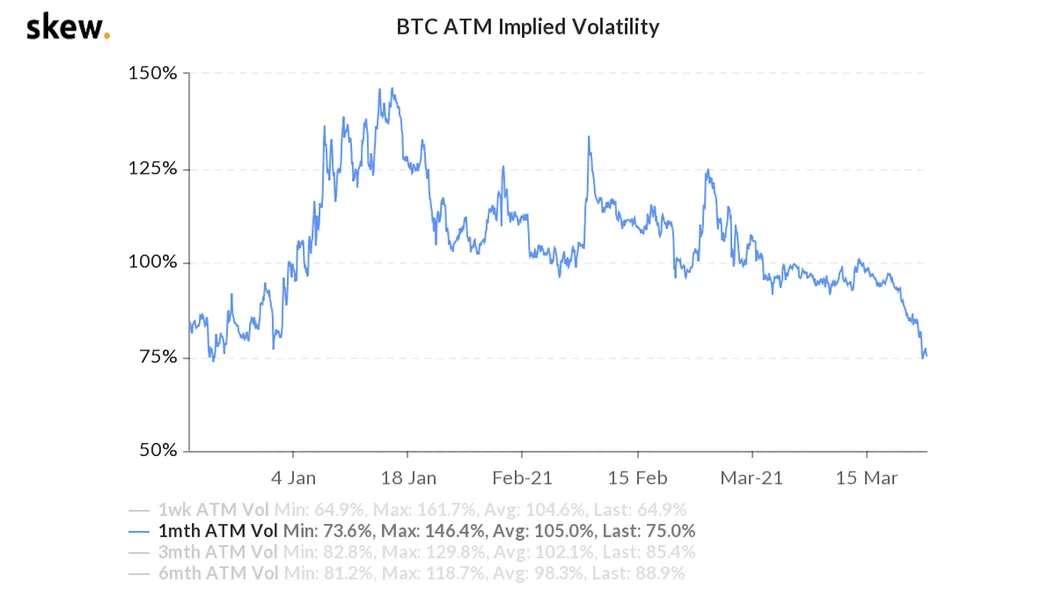
It’s hard to talk about Bitcoin and fail to mention its volatility. The cryptocurrency space is generally highly volatile, which partly makes it an excellent speculative investment. Crypto assets tend to swing in value by up to a thousand percent. These movements have been monumental in creating unimaginable amounts of wealth in just a moment. But again, millions of people have lost their life savings when the prices move against them.
While it’s seemingly one of the fundamental features of Bitcoin, volatility could as well be the cryptocurrency industry’s death. The industry has survived several price crashes, after which the value of coins begins to rebound. However, the price swings kick some investors and companies out of the market, and a rebound is never guaranteed.
For instance, in the ongoing crypto sell-off, high-profile startups like Terraform Labs have closed operations wiping away years of investments. Others like Coinbase have lost 2.2 million customers amid the crypto price crash, while others lay off staff or halt withdrawals. Even if the industry has survived such bearish periods, a significant population continues to lose confidence in Bitcoin and cryptocurrency in general. They are slowly waking up to the fact that Bitcoin lacks intrinsic value. It largely depends on market sentiments and what buyers are willing to pay and can be significantly influenced by the media or whales.
A Hedge Against Inflation?
Bitcoin has been popularized as a safe hedge against inflation, although its performance amid inflation in the traditional economy leaves considerable doubt. As Martin Schmalz, a professor of finance and economics at the University of Oxford, notes, Bitcoin is not an inflationary hedge. Bitcoin’s stability is significantly affected whenever there are changes in interest rates, which happens when inflation is high.
Schmalz’s observation appears true in the ongoing crypto crisis as the prices of Bitcoin sharply drop as the Federal Reserve hikes interest rates.
The Decentralized Finance World
The birth of decentralized finance was one of the critical drivers of Bitcoin’s adoption. Many DeFi projects emerged, forming an ecosystem that provides various financial tools. However, the DeFi ecosystem came with its share of challenges. Most DeFi projects run on the Ethereum blockchain, which has struggled with scalability. It limits the number of transactions that users can execute at a time, so users do not fully realize the potential of DeFi platforms.

While other decentralized finance projects are running on other blockchains like Polkadot, there are still interoperability problems. DeFi users on different blockchains find it challenging to do cross-chain data or asset transfers. Investors have also lost massive amounts of funds on fraudulent DeFi projects.
Security
Initially, Bitcoin was perceived as a secure digital currency on a highly secure distributed ledger network. Blockchain technology goes a long way in ensuring network and asset security using cryptographic algorithms, but it does not achieve 100% security. There have been widespread security breaches in which investors lost millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency. In the most recent case, hackers made away with $100 million in cryptocurrency from Horizon, a blockchain bridge developed by the crypto start-up, Harmony.
Bitcoin Transactions
When Bitcoin began gaining mainstream adoption, many people touted it as an efficient, fast, and low-cost digital currency, making it seem like the future of transacting. However, although many crypto projects provide a digital currency with these features, Bitcoin is not one of them. Bitcoin transactions can take longer and cost more than transactions in conventional financial systems.
Typically, the speeds of transactions in Bitcoin depend on how fast the miners can solve and verify transactions on a block. Note that there is a limit to the number of blocks that can be added in a given time and the number of transactions in a block. Without going into much further detail, the average Bitcoin transaction rate is 7 transactions per second. It is incomparable to the speeds provided by Visa of 2000 transactions per second.
Bitcoin’s Unsustainability
One of the primary reasons behind Bitcoin’s tumble is its energy and environmental problem. Bitcoin mining operations use a mining algorithm known as proof-of-work. The mining process involves solving complex mathematical puzzles using high-power computers, making the process quite energy-intensive. Bitcoin’s annual power consumption is estimated to be 150 terawatt-hours and has sparked fierce debates and rejection of Bitcoin.
In the wake of these sustainability issues, the largest cryptocurrency in the world has suffered significant setbacks that have seen its adoption rates and prices crash significantly. Prices crashed when Elon Musk dropped support for Bitcoin and announced his company would stop accepting Bitcoin as payment over the environmental concerns. Also, Bitcoin is banned in several countries, including China, India, Iran, Bolivia, Russia, Turkey, and Vietnam.
However, there is a glimpse of hope for Bitcoin as companies step forward with green Bitcoin mining operations. EZ Blockchain is one of the top companies changing the future of energy with blockchain technologies. It has one of the largest crypto mining container production in the US, working with renewable energy sources of gas, nuclear, wind, and solar.
We also work with oil and gas producers to put their wasted energy to productive and profitable use.

Summing It Up
Bitcoin promised a new form of finance that employs various technologies to revolutionize how we use and manage our financial assets. The world was quickly embracing the transformative potential of digital currencies and blockchain technology, but how this turns after the economic crisis and the 2022 crypto winter is anyone’s guess. For now, we can only hope that Bitcoin reemerges at some point and prove to be the real future of finance, perhaps after a series of technological revolutions.
Fill out a form and our bitcoin mining expert will contact you.
FREE CONSULTATIONchoose
a miner
profit and
understand data?
business remotely
with EZ Blockchain?
Fill out a form and our bitcoin mining expert will contact you.









